Osteochondrosis in the spine is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur on the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.According to the location of the damage to the spine, they distinguish between osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebrae, osteochondrosis in the chest area and osteochondrosis in the lumbar vertebrae.To diagnose osteochondrosis in the spine, X-ray photography is necessary and in the case of its complications (e.g., hernia of the intervertebral disc) - MRI of the spine.It is widely used in osteochondrosis treatment of the spine as well as in the medication methods, reflexology, massage, manual therapy, physical therapy and physical therapy exercise.
Causes and pathogenesis
To some extent, osteochondrosis of the spine develops in people of all ages and is one of the processes of aging in the body.Changes in atrophy occur earlier or later than the disc, however, injuries, diseases and various spinal overloads contribute to the early occurrence of osteocartilage.Osteochondrosis and osteochondrosis are the most common in the cervical vertebrae.
About 10 osteochondrosis theories have been developed: vascular, hormone, mechanical, hereditary, infectious allergic, etc.However, none of them can fully explain the changes that occur in the spine, but rather they complement each other.
It is believed that the main point of osteochondrosis occurs is the continuous overload of the vertebrae segment, composed of two adjacent vertebrae.Such overloads may be due to motor stereotypes - posture, individual ways of sitting and walking.Poster Disease Sitting in the wrong position, the spine is walking unevenly, causing increased load on the spine's discs, ligaments and muscles.This process may be exacerbated by the characteristics of the spinal structure and the lack of tissue due to genetic factors.Most commonly, vices in this structure are found in the cervical region, leading to vascular disease and early appearance of cervical osteochondrosis.
Overload of osteochondrosis in the lumbar area during severity and elevation is usually associated with its overload.Due to the hydrophilicity of the slurry core located at its center, a healthy intervertebral disc can withstand significant loads.The core contains a lot of water, and it is well known that fluids are rarely compressed.The breakdown of healthy intervertebral discs may occur due to compression of more than 500 kg, while osteocartilage degeneration leads to changes in the intervertebral disc, which is compressed to 200 kg.The 200kg load is experiencing the waist of a spine weighing 70kg when it loads 15kg of cargo in an inclined position of 200kg.Such a huge pressure is due to the lower size of the pulp core.As the inclination increases to 700, the load on the disc will be 489 kg.Therefore, the first clinical manifestation of lumbar osteochondrosis that occurs during or after weight lifting, housework, weeding in the garden, etc.
The destruction of connective tissue of the annulus of the intervertebral discs, ligaments and capsules can lead to the response of the immune system and the development of sterile inflammation, which occurs with the swelling of the phase and its surrounding tissue.Due to the displacement of the vertebrae, the capsule of the planar joint is stretched, and the disc altered in the disc cannot be firmly fixed by the body adjacent to the vertebrae.Instability forming spinal segments.Due to instability, the spinal nerve can be invaded with the development of glomerulonephrosis.In the osteocartilage of the cervical spine, this usually occurs when the head turns, the osteocartilage of the sloping area of the waist becomes - during the sloping of the body.Functional blocks of vertebral motion segments can be formed.This is due to reduced compensation for vertebrae.
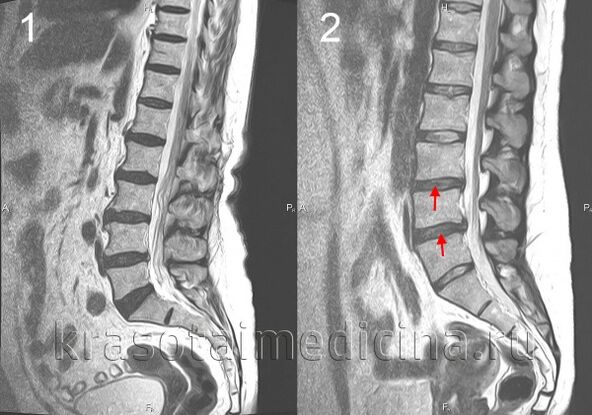
When the disc moves backward, the posterior longitudinal ligament ruptures and the herniation of the disc in the spinal canal, a herniation of the disc.If the nucleus of the intervertebral disc is squeezed out in the cerebrospinal cord canal at the same time, this hernia is called an explosion.This hernia has a much greater severity and duration of pain than the pain that is not exploded.Hernia in the intervertebral disc can cause radiation syndrome or compression of the spinal cord.
In osteocartilage, bone tissue growth occurs with the formation of bones in the vertebrae.Bone plants can also cause compression of the spinal cord or cause the development of radiation syndrome.
Symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis
The main symptom of spinal osteochondrosis is pain.The pain can be sharp and rapid at high intensity, which increases with minimal movement in the affected segment, thus putting the patient in a forced position.Therefore, with the osteocartilage degeneration of the cervical spine, the patient fixes the head in a position with minimal pain and cannot rotate, and the osteocartilage in the chest area increases even with deep breathing, and it is difficult to sit, get up and walk in the tumor area of the lumbar osteocartilage bone marrow.This pain syndrome is a characteristic of compressing the spinal nerve.
In about 80% of the cases, there are constant properties and moderate intensity dull pain.In this case, after the examination, the doctor must distinguish the manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis from myositis in the back muscles.The stupid pain of osteochondrosis is caused by excessive muscle tone, vertebrae changes in the disc, or significant stretching of the disc.In patients with this pain, there is no forced position, but the limitations of movement and physical activity are revealed.Patients with cervical osteocartilage degeneration avoid sharp turns and tilted tilts of the waist, osteochondria of the lumbar osteocartilage bone - sit slowly to avoid tilting the body.
Complications of spinal osteochondrosis
Complications of osteochondrosis are associated with hernia in the intervertebral disc.These include compression of the spinal cord, characterized by numbness, weaknesses in certain muscle groups in certain limbs (depending on the level of compression), resulting in muscle atrophy, tendon reflexes, urination and the emergence of defects.Vertebral hernia may cause arterial compression and form an ischemia area (spinal cord infarction) as nerve cells die.The emergence of neurological defects (impaired movement, sensitivity, nutritional diseases) corresponding to the level and prevalence of ischemia is manifested.
Diagnosing osteochondral disease in the spine
The diagnosis of spinal osteochondrosis is performed by a neurologist or a vertebral doctor.In the initial stage, the spine's X-ray was performed in 2 projections.If necessary, they can shoot individual spinal segments and shoot in other predictions.To diagnose vertebral hernia, spinal cord status was used and complications of osteochondrosis, magnetic and resonance tomography (spine MRI) were detected.MRI plays an important role in the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis and other spinal diseases: tuberculous spondylitis, osteomyelitis, tumors, ankylosing spine, rheumatism, infectious lesions.Sometimes, polio acid is required to be excluded when the cervical vertebrae changes are complex.In some cases, bone marrow science is shown if MRI is not possible.
Targeted study of the affected intervertebral disc using records.Electrophysiological studies are used to determine the extent and localization of neural pathway damage to monitor its recovery process during treatment.
Treatment of osteochondral disease in the spine
In the acute period, peace is shown in the affected vertebral movement segments.To do this, osteocartilage degeneration of the cervical spine was used, fixed with Chantz collar, and with lumbar osteochondrosis - waist - bed rest.For intervertebral segment instability, fixation is also osteochondrosis in the cervical area.
In the drug treatment of osteochondrosis, non-replacement anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): diclofenac, aniamide sulfuric acid, Lornoxicam, Meloxicam.Due to strong pain syndromes, for example, analgesics show analgesic central effects of fluportin.To relieve muscle voltage, use muscle relaxants - thyroxine, thiazolidine.In some cases, it is recommended to prescribe anticonvulsants - Carbamazepine, Gabapentin; antidepressants, which prefer the reverse capture inhibitor of serotonin (Cerseralin, Paroxetine).
If radiation syndrome occurs, hospitalization is indicated.Glucocorticoids may be introduced locally to target the treatment of edema and use traction.It is widely used in the treatment of osteochondrosis, physical therapy, reflexology, massage, and physical therapy exercises.The use of manual therapy requires clear adherence to its implementation techniques and special caution in the treatment of cervical osteocartilage.
Spine surgery mainly indicates significant compression of the spinal cord.It includes removing hernia from the intervertebral disc and decompression of the spinal canal.Microresection can be performed, laser reconstruction of the disk, and replacement of the affected disk with implants, stabilizing spinal segments.